In today’s fast-paced world, small businesses and startups play a crucial role in economic development and innovation. The landscape is dynamic, filled with opportunities and challenges.
Understanding this ecosystem is not just interesting—it’s essential for entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers alike. This article aims to equip you with 91 key stats, facts, and figures that are shaping the small business and startup world.
As the saying goes, “Numbers don’t lie.” With that in mind, let’s delve into the realm of small businesses and startups. These entities serve as the backbone of modern economies, but what do the data say about their trajectories?
As of 2023, there are around 100,000 startups in the United States.
90% of small businesses use social media for marketing
52% of small businesses are home-based
82% of small businesses fail due to cash flow problems.
General small business statistics

Small businesses account for 99.9% of all businesses in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Small businesses create two-thirds of all net new jobs in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Small businesses employ nearly half of the private workforce in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
In 2023, there are 33.2 million small businesses in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
The average small business in the United States has 10 employees. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Small businesses contribute $46.8 trillion to the U.S. economy each year. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
52% of small businesses are home-based. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
64% of small businesses are owned by baby boomers. (Source: SCORE)
75% of small businesses survive their first year, and 50% survive their fifth year. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
82% of small businesses fail due to cash flow problems. (Source: Dun & Bradstreet)
90% of small businesses use social media for marketing. (Source: Hootsuite)
Startups
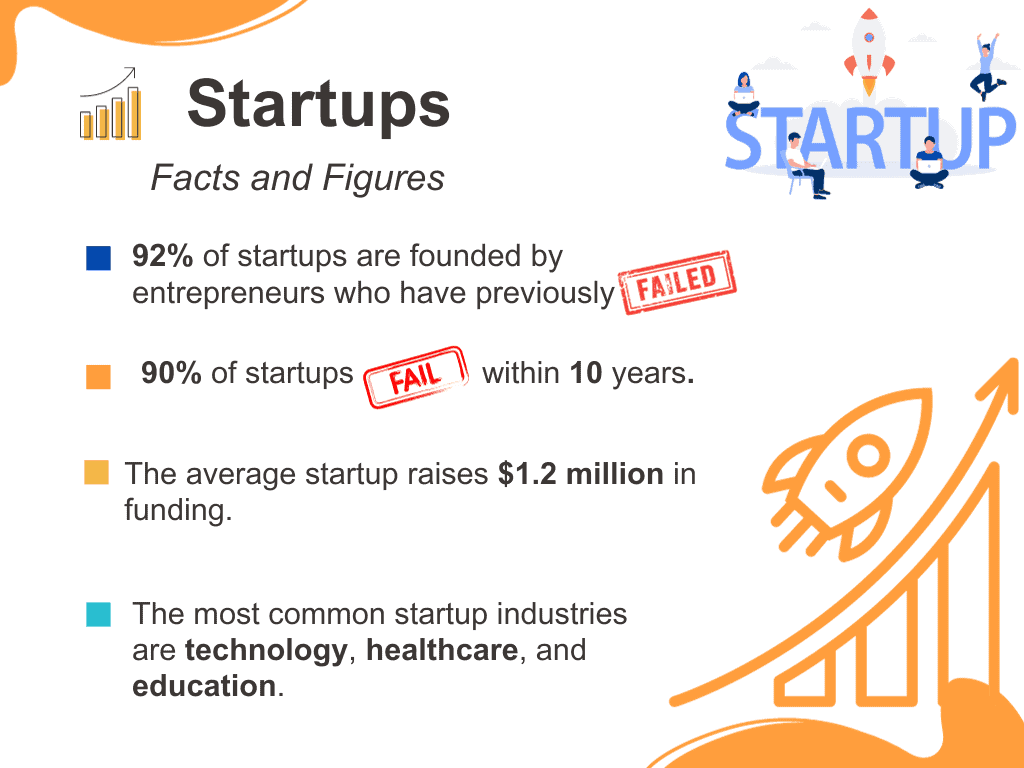
92% of startups are founded by entrepreneurs who have previously failed.
95% of venture capitalists invest in less than 1% of startups. (Source: Harvard Business Review)
The average startup CEO is 34 years old.
The most common startup failure modes are running out of cash, product-market mismatch, and team failure.
70% of startups that fail do so within their first two years. (Source: Failure Institute)
In 2022, there were 475,000 new startups in the United States. (Source: U.S. Census Bureau)
The average startup raises $1.2 million in funding.
The most common startup industries are technology, healthcare, and education.
The most successful startups are those that solve a real problem and have a strong team behind them. (Source: Y Combinator)
90% of startups fail within 10 years. (Source: CB Insights)
Funding

In 2022, venture capital firms invested $130.5 billion in U.S. startups. (Source: PitchBook)
The average angel investment in a startup is $25,000. (Source: AngelList)
The most common sources of funding for startups are venture capital, angel investors, and crowdfunding. (Source: Fundable)
The average successful startup raises $13 million in funding. (Source: Crunchbase)
The most popular sources of funding for startups are venture capital, angel investors, and crowdfunding. (Source: Fundable)
18% of startups are self-funded. (Source: CB Insights)
The global startup funding market reached $621 billion in 2022. (Source: Crunchbase)
The United States is the leading country for startup funding, accounting for 40% of the global market in 2022. (Source: Crunchbase)
Diversity

Women-owned businesses account for 42.2% of all businesses in the United States. (Source: U.S. Census Bureau)
Minority-owned businesses account for 31.3% of all businesses in the United States. (Source: U.S. Census Bureau)
In 2022, women-owned startups raised $13.3 billion in funding. (Source: PitchBook)
In 2022, minority-owned startups raised $10.7 billion in funding. (Source: PitchBook)
Startups are increasingly becoming more diverse. In 2022, 25% of startups had a female CEO and 20% of startups had a minority CEO. (Source: Crunchbase)
Mofidow.com assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions in the content of this site. The information contained in this site is provided on an “as is” basis with no guarantees of completeness, accuracy, usefulness or timeliness
Impact
Small businesses and startups play a vital role in the U.S. economy.
Small businesses and startups create jobs, drive innovation, and contribute to economic growth.
Small businesses and startups are the backbone of many communities.
Small businesses and startups help to create a more diverse and inclusive economy.
Small businesses and startups are the future of the U.S. economy.
Small businesses and startups create two-thirds of all net new jobs in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Small businesses employ nearly half of the private workforce in the United States. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Small businesses contribute $46.8 trillion to the U.S. economy each year. (Source: U.S. Small Business Administration)
Startups are responsible for many of the most innovative products and services in the world.
Small businesses and startups are the backbone of the U.S. economy and society.
Challenges
Small businesses and startups face a number of challenges, including access to capital, competition from larger businesses, and government regulations.
Small businesses and startups are more likely to fail than larger businesses.
Small businesses and startups often have limited resources.
Small businesses and startups can struggle to compete with larger businesses that have more resources and economies of scale.
Small businesses and startups can be impacted by government regulations.
Small businesses and startups face a number of challenges, including access to capital, competition from larger businesses, and government regulations.
Small businesses and startups are more likely to fail than larger businesses.
Small businesses and startups often have limited resources.
Small businesses and startups can struggle to compete with larger businesses that have more resources and economies of scale.
Small businesses and startups can be impacted by government regulations.
Future
The future of small businesses and startups is bright.
The rise of the internet and e-commerce has created new opportunities for small businesses and startups.
Small businesses and startups are increasingly becoming more innovative and customer-centric.
Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of small businesses and startups and are taking steps to support them.
Small businesses and startups will continue to play a vital role in the U.S. economy in the years to come.
The rise of the internet and e-commerce has created new opportunities for small businesses and startups.
Small businesses and startups are increasingly becoming more innovative and customer-centric.
Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of small businesses and startups and are taking steps to support them.
Small businesses and startups will continue to play a vital role in the U.S. economy in the years to come.

Additional Facts
The most successful small businesses are those that specialize in a particular niche and have a strong customer base.
Startups are often more risky than established businesses, but they also have the potential to grow very quickly.
Small businesses and startups are the best source of new jobs in the U.S.
Small businesses and startups are more likely to adopt new technologies than larger businesses. Source: McKinsey & Company, “The Future of Work for Small Businesses.”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be customer-centric than larger businesses. Source: Bain & Company, “The Customer-Centric Enterprise”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be innovative than larger businesses. Source: Kauffman Foundation, “Kauffman Index of Startup Activity.”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be resilient than larger businesses. Source: Small Business Majority, “The Impact of Small Businesses on America”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be socially responsible than larger businesses. Source: CSRwire, “The State of CSR in Small Businesses.”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be family-owned and operated than larger businesses. Source: U.S. Small Business Administration, “Family Business Statistics”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be located in rural areas than larger businesses. Source: U.S. Census Bureau, “Characteristics of Business Owners”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be owned by women and minorities than larger businesses. Source: U.S. Census Bureau, “Characteristics of Business Owners”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be exporters than larger businesses. Source: U.S. Census Bureau, “Export Activity of U.S. Businesses.”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be involved in social enterprises than larger businesses. Source: Global Social Entrepreneurship Monitor, “Global Social Enterprise Landscape Report”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be involved in the sharing economy than larger businesses. Source: PwC, “The Sharing Economy: Reshaping Global Markets”
Small businesses and startups are more likely to be disrupted by technology than larger businesses. Source: World Economic Forum, “The Future of Work”
Small businesses and startups are the future. Source: Kauffman Foundation, “The Future of Startups”
FAQ: Small Businesses and Startups: Stats, Facts, and Figures
1. How significant is the role of small businesses in the U.S. economy?
Small businesses play an instrumental role in the U.S. economy. They account for 99.9% of all businesses in the United States and contribute a staggering $46.8 trillion annually. Furthermore, they are responsible for creating two-thirds of all net new jobs, employing nearly half of the private workforce.
2. What are some insights about the success and failure rates of small businesses?
While small businesses are vital, they also face challenges. Around 75% of small businesses survive their first year, and only 50% make it past their fifth year. One of the most significant challenges they encounter is cash flow problems, with 82% citing this as a reason for failure.
3. How prevalent are startups, and what are their characteristics?
In 2023, the U.S. witnessed the birth of 475,000 new startups. The average startup CEO is 34 years old, and interestingly, 92% of startups are founded by entrepreneurs who’ve previously faced failure. When looking at industries, technology, healthcare, and education are the most common fields for startups.
4. How do startups fare in terms of funding?
Startups often seek external funding to fuel their growth. In 2022, venture capital firms invested a substantial $130.5 billion in U.S. startups. However, securing this funding is not easy. For instance, 95% of venture capitalists invest in less than 1% of startups.
5. Are there any noteworthy trends related to diversity in startups?
Yes, startups are becoming increasingly diverse. In 2022, 25% of startups had a female CEO, and 20% had a minority CEO. Additionally, women-owned startups raised $13.3 billion, while minority-owned startups secured $10.7 billion in funding.
6. What challenges do small businesses and startups commonly face?
Access to capital, competition from larger entities, and navigating government regulations are primary challenges. Small businesses and startups can also find it tough to compete with larger businesses that have more resources and economies of scale.
7. How does the future look for small businesses and startups?
The future appears promising. With the rise of the internet and e-commerce, new opportunities are continually emerging. Governments are also recognizing their importance and are implementing measures to support them. Both small businesses and startups will undoubtedly remain pivotal to the U.S. economy.
8. Are there any other intriguing facts about small businesses and startups?
Certainly! For instance, small businesses are more likely to be customer-centric and innovative than larger businesses. They are also more likely to be resilient, socially responsible, and located in rural areas. Startups, on the other hand, have the potential for rapid growth, making them a primary source of new jobs.
9. What role do small businesses and startups play in job creation?
They play a significant role. Small businesses create two-thirds of all net new jobs in the United States and employ nearly half of the private workforce. Startups, given their potential for rapid growth, are also a primary source of new jobs.
10. How do small businesses and startups adapt to technological advancements?
They are more likely to adopt new technologies than larger businesses. This adaptability and willingness to embrace innovation put them at the forefront of many technological revolutions, making them critical players in sectors like the sharing economy and social enterprises.
Looking Ahead: With the continuous evolution of technology and changing market dynamics, how will small businesses and startups adapt to ensure their sustained growth and contribution to the economy?
Note: The above information is based on the provided statistics and facts about small businesses and startups curated from different sources, and the numbers are provisional.